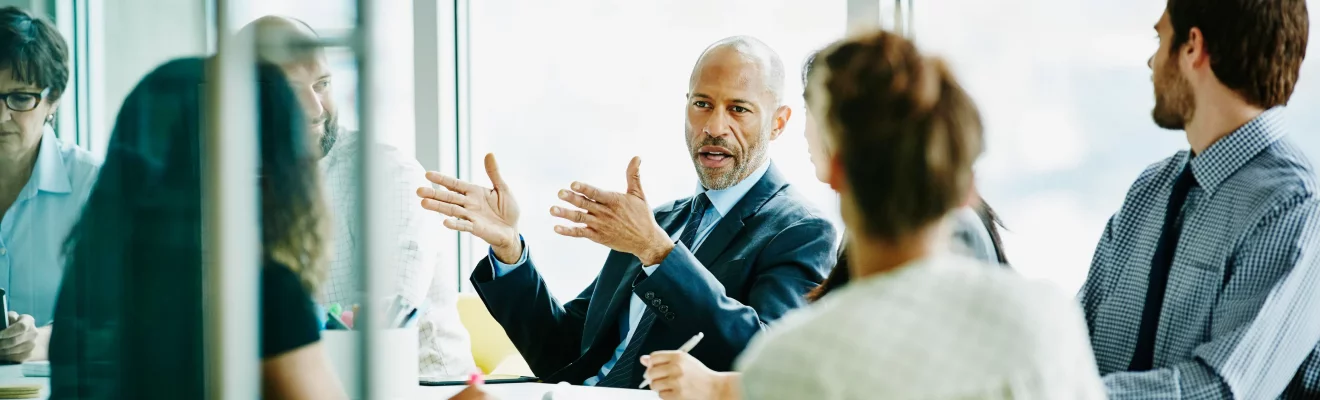
Saudi Arabia has announced a new legal update that expands job opportunities for people holding dependent visas. According to Cabinet Resolution No. 831, issued on September 10, 2025, the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Development (HRSD) now has full authority to issue and manage work permits for dependents living in the Kingdom.
This means that dependents of expatriate workers can now work legally in selected sectors. The new regulation not only supports the Saudi Vision 2030 goals but also improves family stability and helps employers access more skilled workers already residing in Saudi Arabia.
Let’s explore the reasons behind this decision, who can apply, and how dependents can successfully get their work permits approved.
Why Saudi Arabia Allows Dependent Visa Holders to Work
Saudi Arabia is continuously working to attract, retain, and develop skilled professionals in its labor market. Many expatriates in the Kingdom have family members with valuable qualifications but are unable to work because of visa restrictions.
Allowing dependents to work helps solve this issue. It provides economic stability for families, increases labour market flexibility, and supports local businesses by reducing the need to hire from abroad.
This change also aligns with the skill-based work permit system introduced for 2025, which connects job roles to specific skill levels. Under this system, work permits are categorized into high-skill, skilled, and basic-skill groups.
The HRSD, in partnership with the Ministry of Interior, ensures that this policy balances economic needs, family welfare, and national goals.
Eligibility for Dependent Visa Work Permit in Saudi Arabia
Not all dependents qualify for work permits. The eligibility depends on relationship, residency status, and qualifications.
- Qualified Family Members:
Spouses of expatriate workers holding valid work permits
Children who meet the age and dependency criteria
Other dependents recognized under Saudi immigration regulations - Residency Requirements:
The applicant must have a valid dependent visa and iqama
There should be no labor or residency law violations
Sponsorship details must be up to date - Skills and Qualifications:
The applicant must have education and professional certifications relevant to the job they are applying for
For some professions, additional licenses or local approvals may be required
The HRSD may update these eligibility rules periodically. It’s best to confirm the latest requirements before applying.
Jobs and Sectors Open for Dependent Workers in Saudi Arabia
The HRSD will define which sectors are open for dependent workers. Generally, the approved sectors are those that face skill shortages and require experienced professionals.
Open Sectors:
Healthcare: Doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and technicians are in high demand as Saudi Arabia continues to expand its medical infrastructure.
Education: Teachers, administrators, and trainers are needed for schools and private institutions.
Professional Services: Engineers, accountants, consultants, lawyers, and IT specialists.
Hospitality and Tourism: Hotel managers, event coordinators, and customer service professionals.
Retail: Specialized sales roles requiring communication and product knowledge skills.
Restricted Sectors:
Some government, military, and security positions remain restricted to Saudi nationals.
Entry-level or basic-skill roles might have limited availability depending on Saudization targets and market needs.
How to Apply for a Dependent Visa Work Permit in Saudi Arabia
Getting a dependent work permit is a straightforward but detailed process. It involves both the applicant and the employer working together under HRSD guidelines.
Step 1: Prepare Your Documents
You will need a valid passport, iqama, dependent visa copy, educational certificates, professional licenses, and approval from your sponsor. Employers may also require attested copies of your documents.
Step 2: Find an Eligible Employer
Your employer must be registered with HRSD and meet Saudization requirements. The employer will initiate your application by confirming that your position falls within approved job sectors.
Step 3: Apply through Official Portals
Applications can be submitted through Absher for residency services and Qiwa for employment-related services. Authentication through Nafath is required for access.
The HRSD will review your application, while the Ministry of Interior verifies your residency records.
Step 4: Pay the Fees
Work permit fees for dependents are generally similar to those for regular expatriates. The cost depends on the job category, duration, and sector. Most employers cover these expenses.
Step 5: Receive Work Authorization
Once approved, you will receive work authorization linked to your iqama. The document includes your job title, employer name, and expiration date. You must maintain legal residency and follow all employment rules.
If you decide to switch jobs, a new application must be submitted, and both your current and new employers must coordinate with the HRSD.
Talk to an Expert
Applying for a dependent visa work permit in Saudi Arabia can be a complex process if you are unfamiliar with the regulations. Consulting with a business setup expert can make the process smoother and faster. Experts can help you understand the latest HRSD requirements, prepare the necessary documents, and ensure your application is compliant.
Conclusion
The new dependent visa work permit policy in Saudi Arabia represents a major step forward in creating a more flexible and inclusive workforce. It benefits both expatriate families and employers by opening up more career opportunities and utilizing local talent already present in the Kingdom.
As Saudi Arabia continues its economic transformation under Vision 2030, these reforms strengthen the job market, improve family well-being, and help companies access a wider talent pool.
If you need guidance on applying for a dependent visa work permit or understanding the latest HRSD policies, Areeco is here to assist you. Our team provides expert support for business setup, visa services, and regulatory compliance in Saudi Arabia.