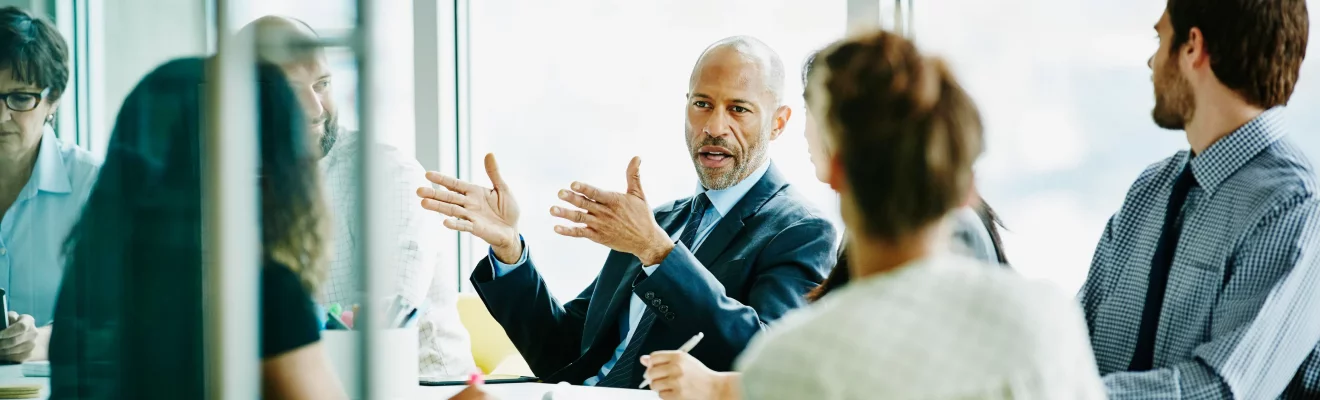
If you’re planning to start a business in Saudi Arabia — whether you’re a foreign investor or a local entrepreneur understanding the difference between a MISA License and a Commercial Registration (CR) is one of the most important steps in the company formation process. While these terms are often used together, they serve distinct purposes in establishing and operating a business within the Kingdom.
In this comprehensive guide, we explain what each license means, highlight the key differences between them, and clarify why both are essential when obtaining a business license in Saudi Arabia, while also exploring the roles of the ministry of trade and investment, the ministry of economy and planning, and the ministry of energy industry & mineral resources.
What Is a MISA License?
A MISA License is a business license issued by the Ministry of Investment — sometimes referred to as MISA which authorizes foreign investors to invest and operate in Saudi Arabia with full compliance under the Kingdom’s foreign investment rules.
This investment license essentially acts as your entry permit into the Saudi market. It grants legal permission to set up your business and pursue your selected business activities under a designated investment category. Without it, foreign entities cannot proceed with forming a company, opening a bank account, or hiring employees.
Key Features of a MISA License
Issued by: Ministry of Investment (MISA) — a division of the ministry of trade and investment focused on attracting foreign investment.
Purpose: Grants legal approval for a foreign investor to invest and establish a business in the Kingdom.
Ownership: Enables 100% foreign ownership in most sectors.
Benefits:
Enables visa issuance and sponsorship for employees.
Allows opening business bank accounts.
Provides access to government incentives and investment support.
Aligns your project with national strategies like Vision 2030.
In essence, the MISA license is the first mandatory step before any formal company registration if you are a foreign investor.
What Is Commercial Registration (CR)?
Once you have your MISA License, the next essential step is obtaining a Commercial Registration (CR) also called a trade license from the Ministry of Commerce.
The CR is your company’s legal identity in Saudi Arabia. It confirms that your business has a registered name, defined activities, a legal structure, and an official registration number — essentially giving your business the authority to operate legally within the Kingdom.
Key Features of Commercial Registration
Issued by: Ministry of Commerce part of the ministry of economy and planning ecosystem that oversees business registration and regulatory compliance.
Purpose: Legally establishes your business entity and lets it operate commercially in Saudi Arabia.
Scope:
Enables issuing invoices.
Allows you to enter into contracts.
Required for opening corporate bank accounts.
Necessary for hiring staff and registering with government platforms (like ZATCA, Qiwa, and GOSI).
Applicable to: All companies, both foreign and local.
Without a CR, your business is not legally recognized and cannot operate, even if you have obtained a MISA License as a foreign investor.
MISA License vs Commercial Registration: What’s the Difference
Now that we understand each in isolation, let’s break down the main differences between them:
Authority and Issuing Bodies
MISA License: Issued by the Ministry of Investment — the foreign investment authority within the ministry of trade and investment.
Commercial Registration: Issued by the Ministry of Commerce — aligned with broader economic governance under the ministry of economy and planning.
Purpose
MISA License: Authorizes foreign investment and 100% ownership across most sectors.
Commercial Registration: Legally registers your business entity and allows it to conduct operations.
Who Needs It
MISA License: Required only for foreign investors looking to establish a business in Saudi Arabia.
Commercial Registration: Required for all businesses — both foreign and local — to operate.
When It Is Needed
MISA License: First step for foreign investors.
Commercial Registration: Obtained after the MISA license (for foreign entities).
Legal and Practical Impact
MISA License: Allows investment and sets up eligibility but does not permit commercial operations on its own.
Commercial Registration: Gives your business legal status and operational ability in Saudi Arabia.
How They Work Together in the Business Setup Process
In simple terms:
Apply for the MISA License. This gives you permission to invest and is usually the first checkpoint for foreign investors.
Reserve your business name and prepare documents. This step involves notarized articles of association, shareholder information, and approved business activities.
Obtain Commercial Registration (CR). This step formally establishes your company as a legal entity.
Register for taxes and payroll. Submit your CR to authorities like ZATCA (tax authority) and GOSI (social insurance).
Open bank accounts and start operations. This is when your business can legally trade, hire staff, and execute contracts.
Cost and Timelines
Costs for MISA and CR vary, but typically include:
Annual MISA license fees.
Commercial Registration fees upon issuance.
Document attestation and legal fees.
Office lease and capital deposit requirements.
Processing times range from a few weeks (for MISA) to a few days (for CR), depending on documentation and accuracy.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a MISA License vs Commercial Registration in saudi arabia is essential for anyone planning to establish a business in Saudi Arabia. Although both are mandatory steps in the company formation process, they serve entirely different functions and cannot substitute for one another. As an expert business consultant company, we help investors clearly navigate these requirements to ensure full compliance and a smooth business setup journey